
Payroll outsourcing services in India go beyond just calculating employee salaries. They help employers manage the complexities of statutory requirements, tax laws, and labour regulations. Failure to comply can lead to penalties, legal issues, and employee dissatisfaction.
For business owners and HR teams, understanding the key payroll compliance requirements is essential to run smooth and lawful operations.
1. Understanding Payroll Compliance in India
Payroll compliance refers to following all relevant laws and regulations related to employee compensation, statutory deductions, tax filings, and reporting. In India, payroll compliance is governed by several laws, including
- The Employees’ Provident Funds and Miscellaneous Provisions Act, 1952 (EPF)
- The Employees’ State Insurance Act, 1948 (ESI)
- The Income Tax Act, 1961 (for TDS on salaries)
- The Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972
- The Payment of Bonus Act, 1965
- The Labour Welfare Fund Act (varies by state)
- The Shops and Establishment Act (varies by state)
- Professional Tax laws (state-specific)
- The Minimum Wages Act, 1948
To ensure compliance, employers using payroll outsourcing services in India must stay updated on these laws, as amendments occur frequently.
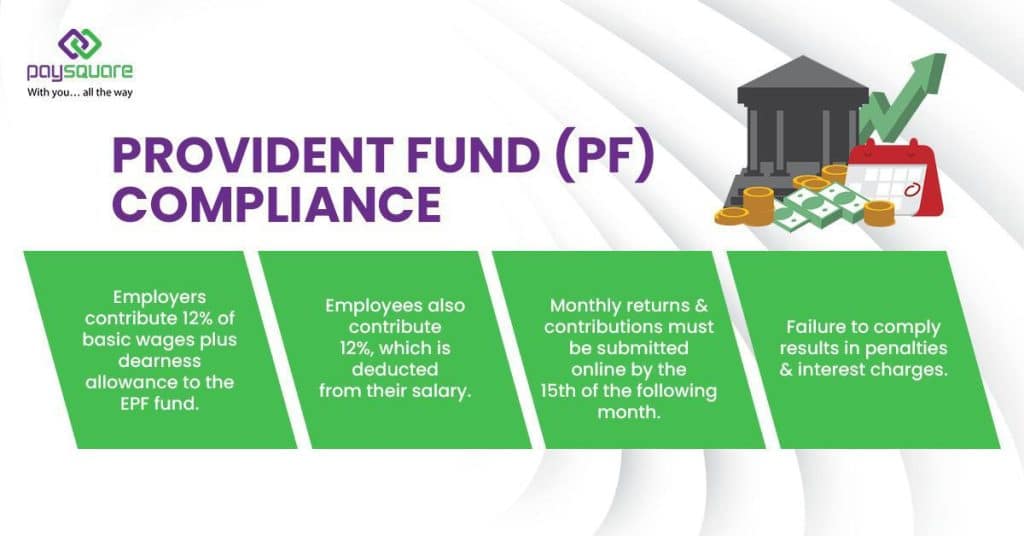
Provident Fund (PF) Compliance
The Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO) manages the Employees’ Provident Fund (EPF), a retirement benefit scheme. Employers who have 20 or more employees must register and contribute to the EPF.
Key Points:
- Employers contribute 12% of basic wages plus dearness allowance to the EPF fund.
- Employees also contribute 12%, which is deducted from their salary.
- You must submit monthly returns and contributions online by the 15th of the following month.
- Failure to comply results in penalties and interest charges.
Proper calculation and timely submission of PF contributions are crucial for compliance.
Employees’ State Insurance (ESI)
ESI provides medical benefits and insurance coverage to employees earning below a specified wage threshold. Employers with 10 or more employees must register for ESI.
Key Points:
- Employers contribute 3.25% of wages; employees contribute 0.75%.
- Wages include basic salary, dearness allowance, and other allowances.
- Monthly contributions and returns must be filed online.
- Non-compliance can lead to fines and prosecution.
ESI compliance protects employees’ health benefits and helps avoid legal complications.
Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) on Salaries
Employers are responsible for deducting income tax (TDS) from employee salaries as per the Income Tax Act.
Key Points:
- TDS must be calculated according to the applicable income tax slabs.
- Employees submit Form 12B or Form 16 to declare exemptions and deductions.
- Monthly TDS must be deposited with the government by the 7th of the following month.
- An annual TDS return must be filed.
Proper TDS management ensures employees do not face tax issues later, and the employer avoids penalties.
Labour Welfare Fund (LWF)
The Labour Welfare Fund is a small contribution by employers and employees toward employee welfare schemes, such as housing, education, and medical aid.
Key Points:
- Applicable in states such as Maharashtra, Gujarat, and Kerala.
- The contribution amount and frequency vary by state.
- Employers must register, deduct, and deposit LWF contributions timely manner.
Compliance avoids penalties and promotes employee welfare.
Salary Components and Minimum Wages Act
Employers must structure salary components to comply with the state government’s minimum wage laws. The Minimum Wages Act ensures employees are paid at least the prescribed minimum wages for their skill category.
Key Points:
- Minimum wage rates differ by state, industry, and job category.
- Salary components like basic pay, HRA, and allowances should align with minimum wage guidelines.
- Failure to pay minimum wages is a legal offence.
Regularly reviewing wage structures according to changes in minimum wages helps avoid legal trouble.
Maintaining Payroll Records
Employers are legally required to maintain detailed payroll records for each employee, including:
- Attendance and leave records
- Salary payment details and slips
- Statutory deductions and contributions
- Tax filings and returns
Records must be kept for a minimum period (usually 3 to 5 years) as prescribed under various laws. Proper documentation helps during audits and inspections.
Handling Employee Exit and Full and Final Settlement (FnF)
When an employee leaves, employers must complete a full and final settlement, including pending salary, gratuity, leave encashment, and other dues.
Key Points:
- Settlement must be accurate and timely.
- You must make deductions for taxes and advances.
- The employer may require the issuance of relieving letters and experience certificates.
- Proper compliance avoids disputes and legal cases.
Payroll outsourcing services in India help manage employee exits smoothly through an efficient payroll process.
How Employers Can Ensure Payroll Compliance
- Stay Updated: Regularly follow government notifications and amendments to payroll laws.
- Use Payroll Software: Implement software that automates calculations, deductions, and filings.
- Train HR Staff: Ensure the HR and finance teams understand statutory requirements.
- Conduct Regular Audits: Internal checks help identify and correct errors early.
- Seek Expert Help: Consider payroll outsourcing or consulting with professionals.
Why Payroll Outsourcing Helps with Compliance
Using payroll outsourcing services in India from expert providers like Paysquare can help simplify compliance. These firms:
- Monitor changes in laws and update processes accordingly.
- Use specialised software for accurate calculations and filings.
- Manage all statutory registrations, returns, and payments.
- Offer secure data management and confidentiality.
- Provide reports and support for audits.
This reduces the burden on internal teams and lowers compliance risks.
Paysquare: Simplifying Payroll Compliance for Indian Employers
With over 24 years of experience and thousands of satisfied clients, Paysquare offers comprehensive payroll outsourcing services tailored to Indian businesses. Their expertise covers:
- End-to-end payroll processing and salary calculations
- Timely PF, ESI, TDS, and professional tax filings
- Accurate full and final settlements
- Customised reports and employee self-service portals
- Dedicated support and compliance guidance
Outsourcing Payroll services to Paysquare helps your company stay compliant with Indian payroll laws while allowing you to concentrate on your core business activities.
Conclusion
Payroll compliance in India is complex but critical. Employers must understand the key legal requirements around PF, ESI, TDS, minimum wages, and other statutory laws. Maintaining accurate records and filing them promptly can prevent penalties and foster employee trust.
Whether your business has 10 or 1,000 employees, prioritising payroll compliance safeguards your company’s reputation and helps build a positive workplace culture.
Ready to Stay Compliant Without Hassle?
Connect with Paysquare for expert payroll management that meets all Indian compliance requirements. Their team helps you stay updated, avoid errors, and reduce the workload on your HR department.
Contact Paysquare today for a free consultation and experience seamless, reliable payroll services.
